पिछले कुछ वर्षों में Lithium-ion Battery Fire incidents तेज़ी से बढ़े हैं — चाहे वो EV charging stations हों, energy storage systems हों या smartphones और laptops। इन आगों का व्यवहार इतना अलग है कि पारंपरिक categories (Class A, B, C, D) उन्हें सही तरीके से cover नहीं कर पा रही थीं।
इसी चुनौती को देखते हुए International Organization for Standardization (ISO) ने अपने नए संस्करण ISO 3941:2026 में एक नई श्रेणी Class L Fire जोड़ी है। यह category खास तौर पर Thermal Runaway, Toxic gases और Re-ignition risk जैसी Lithium-ion battery fires की unique problems को address करती है।
Class L fires वे आगें होती हैं जो lithium-ion cells और batteries में होती हैं, जहाँ कोई lithium metal मौजूद नहीं होता। ये electrochemical fires होती हैं जो thermal और chemical instability के कारण फैलती हैं।
इसका मतलब है कि अब fire safety professionals को Lithium-ion incidents के लिए अलग extinguishing strategies, नए Class L Fire Extinguishers और updated Fire Risk Assessment अपनाने होंगे।
Class L Fire का introduction सिर्फ एक नया technical term नहीं है — यह battery safety के लिए पूरी दुनिया में नए युग की शुरुआत है।
Introduction to the New Class L Fire Classification
What is the major update in ISO 3941:2026?
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) ने अपने नए संस्करण ISO 3941:2026 में एक महत्वपूर्ण बदलाव किया है। अब आग की पारंपरिक categories (Class A, B, C, D, K) के साथ एक नई श्रेणी Class L Fire जोड़ी गई है। यह category खास तौर पर Lithium-ion Battery Fires के लिए है।
Why the world needed a dedicated Class L Fire category
Lithium-ion batteries का उपयोग EVs, smartphones, laptops और energy storage systems में तेजी से बढ़ रहा है। इन आगों का व्यवहार सामान्य आग से अलग है — Thermal Runaway, Toxic gas emission और Re-ignition risk इन्हें unique बनाते हैं। पारंपरिक extinguishers और fire categories इन challenges को address नहीं कर पा रही थीं। इसीलिए दुनिया को एक dedicated Class L Fire category की ज़रूरत थी।
Class L Fire का मतलब है कि अब Lithium-ion battery incidents को अलग से classify और handle किया जाएगा। यह fire safety standards में एक बड़ा बदलाव है।
Why Lithium-Ion Batteries are Classified as Class L
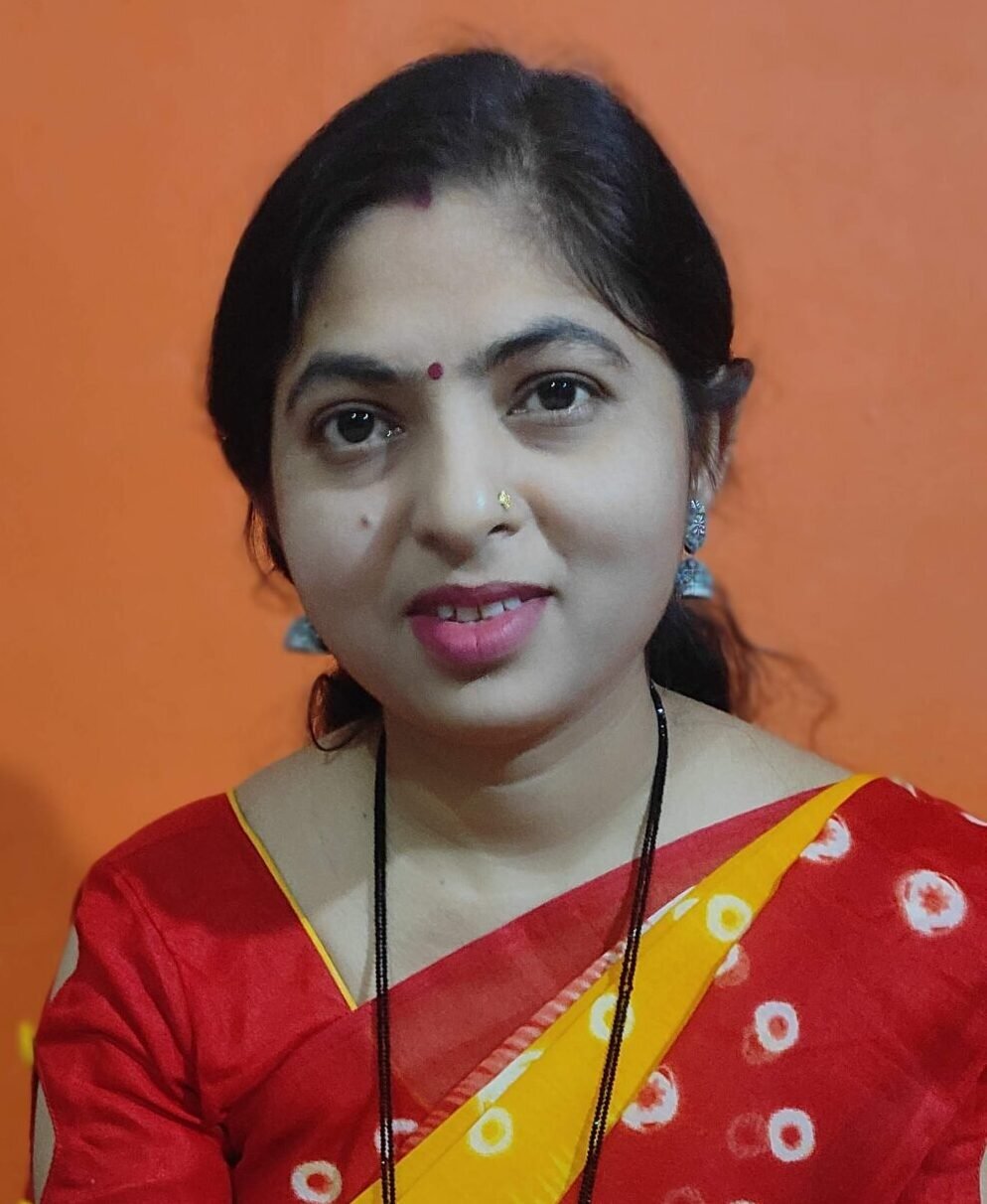
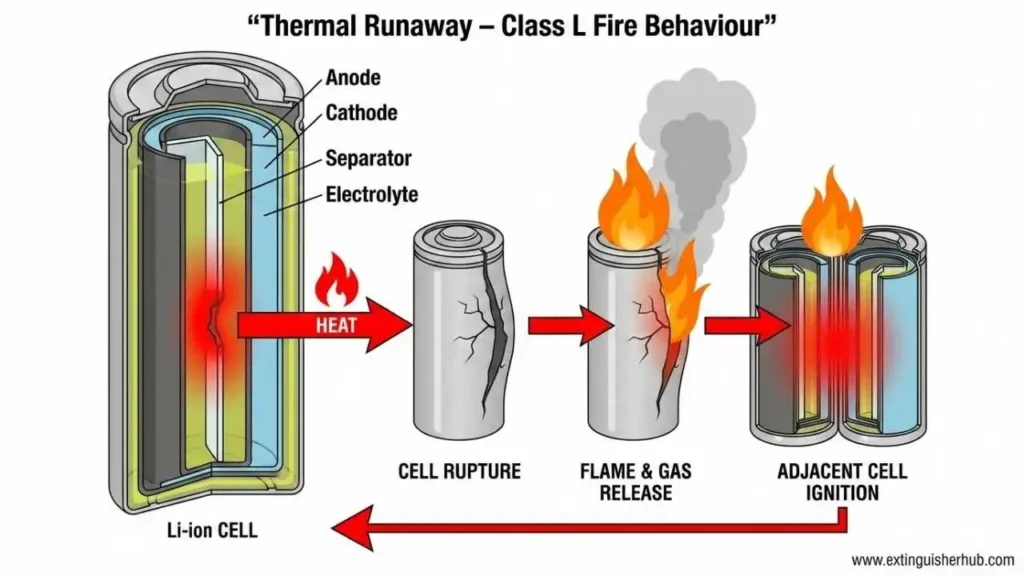
Understanding the science of Thermal Runaway in Class L Fire
Lithium-ion cells में जब Thermal Runaway होता है, तो battery uncontrollable heat generate करती है। यह heat आसपास की cells को भी प्रभावित करती है, जिससे chain reaction शुरू हो जाता है। इस प्रक्रिया में battery pack अचानक flames और high temperature release करता है, जो सामान्य आग से कहीं अधिक खतरनाक होता है।
Why traditional extinguishers fail to control a Class L Fire
पारंपरिक ABC extinguishers या Class D extinguishers Lithium-ion battery incidents पर प्रभावी नहीं होते। Dry powder agents heat को absorb नहीं कर पाते, और आग बुझने के बाद भी cells दोबारा ignite हो सकती हैं। इसी वजह से इस नई category के लिए specialized agents जैसे AVD, F‑500 या Water Mist का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है।
Risks of toxic gases and re-ignition in lithium battery incidents
Lithium-ion battery fires सिर्फ flames ही नहीं, बल्कि toxic gases भी release करते हैं जैसे carbon monoxide और hydrogen fluoride। ये gases confined spaces में serious health hazards पैदा कर सकती हैं। इसके अलावा, extinguishing के बाद भी cells में बची हुई heat re-ignition का खतरा बनाए रखती है। यही कारण है कि इन्हें अलग category में classify करना ज़रूरी था।
Lithium-ion battery fires का behavior पारंपरिक आग से अलग है — thermal runaway, toxic off‑gassing और re‑ignition risk इन्हें unique बनाते हैं। इन्हीं hazards को address करने के लिए Class L classification पेश किया गया।
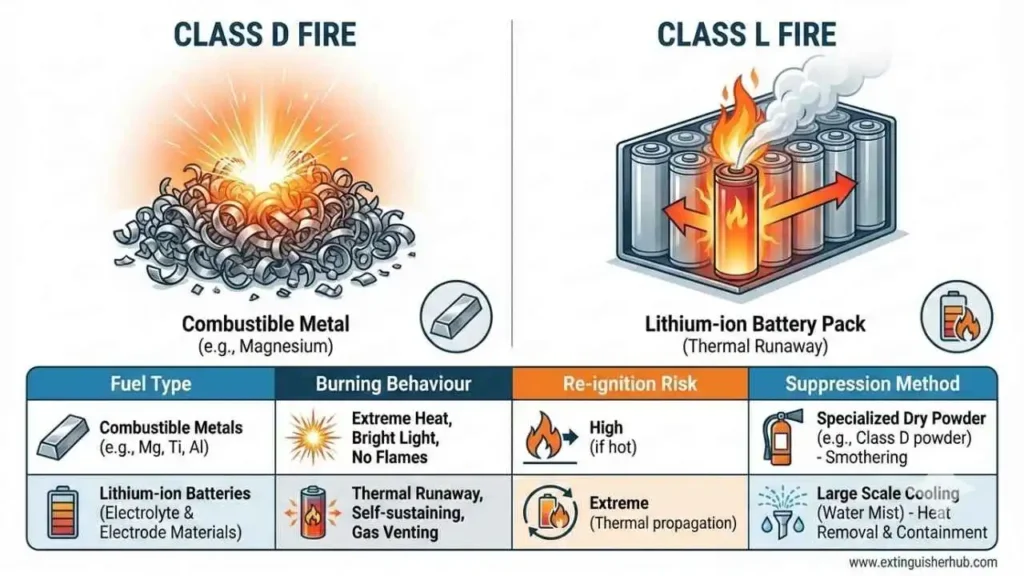
Technical Comparison: Class D vs Class L Fire
Key differences in fuel types and burning behavior
Class D Fires आमतौर पर magnesium, sodium या titanium जैसे combustible metals से जुड़ी होती हैं। वहीं Class L Fires खास तौर पर Lithium-ion battery incidents को cover करती हैं, जहाँ metallic lithium नहीं होता लेकिन thermal runaway और toxic gases का खतरा रहता है। इस वजह से दोनों का burning behavior और extinguishing approach अलग है।
| Aspect | Class D Fire (Metal Fires) | Class L Fire (Lithium-ion Battery Fires) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Magnesium, Sodium, Titanium | Lithium-ion cells (without metallic lithium) |
| Burning Behavior | High temperature, sparks, violent reaction with water | Thermal runaway, jet flames, toxic gases, re-ignition risk |
| Extinguishing Agents | Dry powder agents (sodium chloride, copper powder) | Cooling agents (AVD, F-500, Water Mist) |
| Common Locations | Metal workshops, factories | EVs, smartphones, laptops, energy storage systems |
Why you shouldn’t use a Class D agent on a Class L Fire
Class D agents जैसे dry powder heat को absorb नहीं कर पाते और Lithium-ion cells में बची हुई energy दोबारा ignition कर सकती है। इसलिए Class D Fire extinguishers को Class L incidents पर इस्तेमाल करना खतरनाक हो सकता है। इसके बजाय specialized agents और cooling methods अपनाना ज़रूरी है। अंतरराष्ट्रीय स्तर पर ISO 3941:2026 और NFPA 855 जैसे standards इस बात पर ज़ोर देते हैं।
Class D और Class L दोनों fires अलग fuel sources और hazards से जुड़ी हैं। इन्हें सही तरीके से classify और extinguish करना fire safety professionals के लिए critical है।
Case Studies: Real Incidents of Lithium-Ion Fires
India (Ola EV scooter fires, 2024)
2024 में भारत में Ola Electric scooters से जुड़े कई fire incidents सामने आए। Scooters अचानक आग पकड़ते हुए देखे गए, जिससे EV safety पर गंभीर सवाल उठे। Transport Ministry ने जांच शुरू की और experts ने Thermal Runaway को मुख्य कारण बताया। इसने EV industry को battery design और fire safety standards पर पुनर्विचार करने के लिए मजबूर किया।
Global warehouse ESS fire (2025)
2025 में एक बड़े Energy Storage System (ESS) warehouse में lithium-ion battery fire ने global safety community को हिला दिया। Storage units में thermal runaway शुरू हुआ और fire suppression systems ineffective साबित हुए। इस घटना ने international standards को और मजबूत करने की आवश्यकता पर ज़ोर दिया।
UK audit example (2026)
2026 में UK में एक logistics terminal audit के दौरान inspectors ने पाया कि forklift fleet lithium-ion batteries पर चल रही थी, लेकिन fire response plan outdated था। Warehouse manager ने dry powder extinguisher दिखाया, जिसे auditor ने ineffective बताया। Audit ने highlight किया कि battery fires को Class L के रूप में अलग से classify करना क्यों ज़रूरी है।
India, Global और UK के case studies दिखाते हैं कि Lithium-ion battery fires अब isolated incidents नहीं रहे। यह एक systemic challenge है जिसके लिए dedicated Class L classification और updated extinguishing strategies ज़रूरी हैं।

Current Status of Class L Fire Classification in India
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) and its alignment with ISO 3941
अंतरराष्ट्रीय स्तर पर ISO 3941:2026 में पहली बार Class L Fire को Lithium-ion battery incidents के लिए अलग category के रूप में शामिल किया गया है। UK जैसे देशों ने इसे पहले ही adopt कर लिया है। भारत में Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) ने अभी तक कोई official notification जारी नहीं किया है कि उन्होंने ISO 3941:2026 को formally adopt कर लिया है। हालाँकि industry experts और regulators इस पर चर्चा कर रहे हैं और भविष्य में alignment की संभावना है। (संदर्भ: IS 2190:2024 BIS Fire Safety Rules)
How Class L Fire rules will impact the Indian EV industry
भारत में EV adoption तेजी से बढ़ रहा है। लेकिन Ola और अन्य EV scooter fires ने battery safety पर गंभीर सवाल उठाए हैं। अगर BIS भविष्य में Class L Fire rules को adopt करता है, तो manufacturers को नए extinguishing solutions, thermal management systems और updated fire risk assessments अपनाने होंगे। यह industry को electrical fire safety के साथ-साथ battery‑specific hazards पर भी ध्यान देने के लिए मजबूर करेगा।
New safety mandates for EV charging stations and battery storage
EV charging stations और large battery storage warehouses भविष्य में Class L Fire के लिए dedicated extinguishers और response plans रखने के लिए बाध्य हो सकते हैं। अंतरराष्ट्रीय standards जैसे ISO 3941:2026 और NFPA 855 इस दिशा में पहले ही कदम उठा चुके हैं। भारत में regulatory adoption होते ही fire safety audits और inspections और भी सख्त हो जाएंगे।
भारत में Class L Fire classification अभी official रूप से लागू नहीं हुआ है। लेकिन EV industry और battery storage sector के लिए यह भविष्य में game‑changer साबित हो सकता है।
Regulatory References for Class L Fire
ISO 3941:2026 — Class L addition
अंतरराष्ट्रीय स्तर पर ISO 3941:2026 में पहली बार Class L Fire को Lithium-ion battery incidents के लिए अलग category के रूप में शामिल किया गया है। यह update fire safety professionals को battery‑specific hazards address करने के लिए नए extinguishing strategies अपनाने की दिशा देता है।
BIS IS 15683 — Indian extinguisher standard
भारत में Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) ने IS 15683 जारी किया है, जो portable fire extinguishers के लिए Indian standard है। हालाँकि इसमें अभी तक Class L Fire का सीधा reference नहीं है, लेकिन future updates में Lithium-ion battery hazards को address करने की संभावना है।
NFPA 855 (US) — Energy Storage Systems safety
अमेरिका में NFPA 855 Energy Storage Systems (ESS) के लिए dedicated safety standard है। यह lithium-ion battery installations में fire prevention, suppression और emergency response protocols को define करता है। Class L Fire का concept NFPA 855 के साथ मिलकर global safety framework को और मजबूत करता है।
ISO 3941:2026 ने Class L Fire को internationally recognize किया है। भारत में BIS standards अभी transition phase में हैं, जबकि US में NFPA 855 पहले से battery storage safety को regulate कर रहा है।
Effective Methods to Handle Lithium-Ion Battery Fires (Class L)
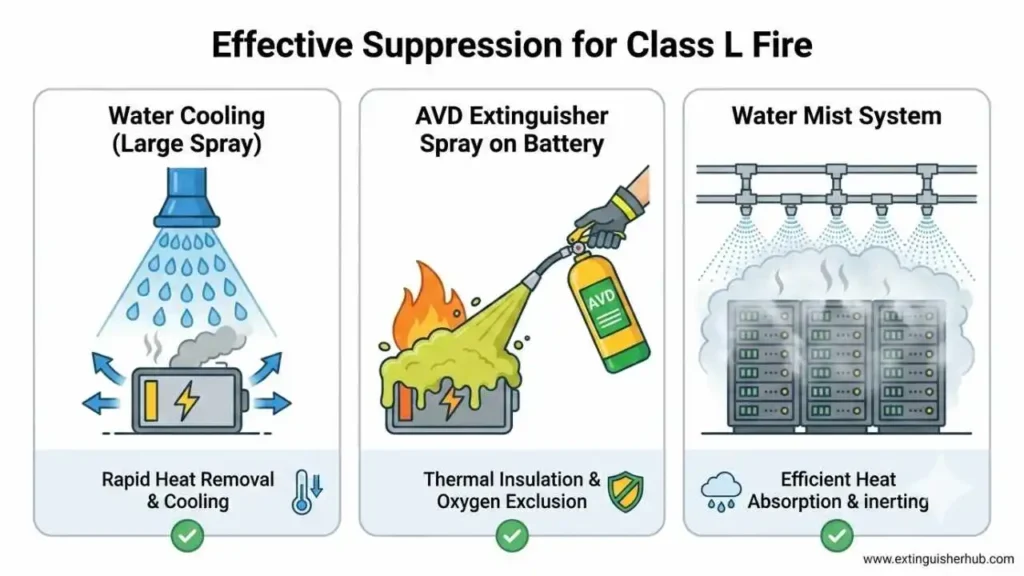
Why intensive cooling is critical in suppression
Lithium-ion battery fires में सबसे बड़ा खतरा Thermal Runaway होता है। अगर cells को तेजी से cool नहीं किया गया, तो chain reaction फैल सकता है और battery pack बार‑बार ignite हो सकता है। इसीलिए intensive cooling methods जैसे water mist या advanced cooling agents fire suppression में critical भूमिका निभाते हैं।
Specialized extinguishing agents: AVD, F‑500, and Water Mist
पारंपरिक extinguishers Lithium-ion fires पर प्रभावी नहीं होते। इसलिए specialized agents का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है: AVD (Aqueous Vermiculite Dispersion) जो cells को encapsulate करके heat absorb करता है, F‑500 encapsulator agent जो flammable vapors को neutralize करता है, और Water Mist systems जो rapid cooling और oxygen displacement दोनों provide करते हैं। ये agents Class L incidents के लिए recommended solutions हैं।
Emergency response guide for EV‑related incidents
EV fires में सबसे पहले area को evacuate करना और toxic gases से बचाव करना ज़रूरी है। Firefighters को protective gear पहनकर specialized extinguishers का इस्तेमाल करना चाहिए। Battery pack को cool करने के बाद monitoring जारी रखनी चाहिए क्योंकि re‑ignition का खतरा बना रहता है। Emergency response plans में clear communication, isolation zones और post‑incident inspection शामिल होना चाहिए।
Lithium-ion battery fires को सिर्फ बुझाना ही काफी नहीं है। Intensive cooling, specialized agents और structured emergency response इन incidents को effectively handle करने के लिए अनिवार्य हैं।
Practical Checklist for Fire Safety Professionals
EV charging station owners
- चार्जिंग पॉइंट पर Class L संगत अग्निशामक उपलब्ध रखें।
- स्टाफ को नियमित रूप से बैटरी आग की घटनाओं को संभालने का प्रशिक्षण दें।
- आपातकालीन शट‑ऑफ सिस्टम और स्पष्ट संकेतक लगाएँ।
- निरीक्षण और अनुपालन रिकॉर्ड बनाए रखें।
Warehouse and ESS managers
- टॉक्सिक गैसों को नियंत्रित करने के लिए वेंटिलेशन सिस्टम अपग्रेड करें।
- Fire Risk Assessment (FRA) को अपडेट करें ताकि बैटरी hazards शामिल हों।
- AVD, F‑500 और Water Mist जैसे विशेष agents स्टोरेज एरिया में रखें।
- स्थानीय फायर डिपार्टमेंट के साथ आपातकालीन अभ्यास करें।
General users
- डिवाइस को ओवरचार्ज न करें और अत्यधिक गर्मी से बचाएँ।
- सिर्फ प्रमाणित चार्जर और एक्सेसरीज़ का उपयोग करें।
- खराब या फूली हुई बैटरियों को अधिकृत केंद्रों पर सुरक्षित रूप से नष्ट करें।
- असामान्य गंध, धुआँ या ओवरहीटिंग पर तुरंत सतर्क रहें।
यह चेकलिस्ट EV स्टेशन मालिकों, वेयरहाउस मैनेजर्स और सामान्य उपयोगकर्ताओं सभी को लिथियम‑आयन बैटरी आग के खतरों के लिए तैयार करती है। हर stakeholder को अपनी जिम्मेदारी निभानी होगी।

The Future of Global Fire Safety
Updates in Fire Risk Assessment (FRA)
भविष्य में Fire Risk Assessment (FRA) को लिथियम‑आयन बैटरी hazards को ध्यान में रखते हुए अपडेट किया जा रहा है। अब FRA में thermal runaway, toxic gas release और re‑ignition जैसे risks को अलग से शामिल किया जाएगा। इससे fire safety professionals को अधिक सटीक और आधुनिक risk profiles तैयार करने में मदद मिलेगी।
New testing protocols for extinguishers
लिथियम‑आयन बैटरी आग के लिए नए testing protocols विकसित किए जा रहे हैं। इनमें AVD, F‑500 और Water Mist जैसे agents को अलग‑अलग scenarios में test किया जा रहा है ताकि उनकी effectiveness को validate किया जा सके। भविष्य में fire extinguishers को सिर्फ traditional fires ही नहीं, बल्कि battery‑specific hazards के लिए भी certify किया जाएगा।
Global fire safety का भविष्य लिथियम‑आयन बैटरी hazards को सीधे address करने पर केंद्रित है। Updated FRA और नए testing protocols fire safety standards को और मजबूत बनाएंगे।
Conclusion: Preparing for the Class L Fire Era
इस पूरे लेख में हमने देखा कि Class L Fire अब केवल एक तकनीकी शब्द नहीं, बल्कि आधुनिक फायर सेफ्टी का महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा बन चुका है। भारत और दुनिया भर में EVs, बैटरी स्टोरेज और चार्जिंग इंफ्रास्ट्रक्चर तेजी से बढ़ रहे हैं, और इनके साथ जुड़े जोखिम भी उतने ही गंभीर हैं।
फायर सेफ्टी प्रोफेशनल्स को अब नए standards, updated FRA, specialized extinguishers और structured emergency response plans को अपनाना होगा। यह बदलाव केवल compliance के लिए नहीं, बल्कि लोगों की सुरक्षा और सस्टेनेबल टेक्नोलॉजी के भविष्य के लिए ज़रूरी है।
फायर सेफ्टी प्रोफेशनल्स को Class L Fire hazards को अपने training, equipment और risk assessment frameworks में तुरंत शामिल करना चाहिए। यही तैयारी हमें आने वाले Class L Fire Era के लिए सुरक्षित बनाएगी।
Frequently Asked Questios
What is Class L Fire?
Class L Fire लिथियम-आयन बैटरी से संबंधित आग के लिए प्रस्तावित नई श्रेणी है। यह पारंपरिक आग से अलग व्यवहार करती है क्योंकि इसमें thermal runaway और दोबारा सुलगने का जोखिम अधिक होता है।
What extinguisher is used for lithium battery fire?
लिथियम-आयन बैटरी आग में मुख्य तरीका है गहन शीतलन (cooling)। पानी, वॉटर मिस्ट या AVD जैसे विशेष एजेंट उपयोग किए जाते हैं। सामान्य ABC या CO₂ हर स्थिति में पर्याप्त नहीं होते।
How is Class L different from Class D?
Class D धातु आग (जैसे मैग्नीशियम) के लिए है, जबकि Class L लिथियम-आयन बैटरी आग के लिए प्रस्तावित है। Class L में अंदरूनी सेल प्रतिक्रिया और re-ignition का खतरा अधिक होता है।
Why lithium battery fires re-ignite?
लिथियम-आयन बैटरी में thermal runaway के कारण अंदर की रासायनिक प्रतिक्रिया जारी रह सकती है, जिससे आग दोबारा जल सकती है, भले ही ऊपर की लपटें बुझ गई हों।
Can water extinguish lithium-ion battery fire?
हाँ, पानी का उपयोग शीतलन के लिए किया जा सकता है, लेकिन पर्याप्त मात्रा में और सही रणनीति के साथ। केवल सतही बुझाव से पूरी तरह नियंत्रण नहीं होता।

